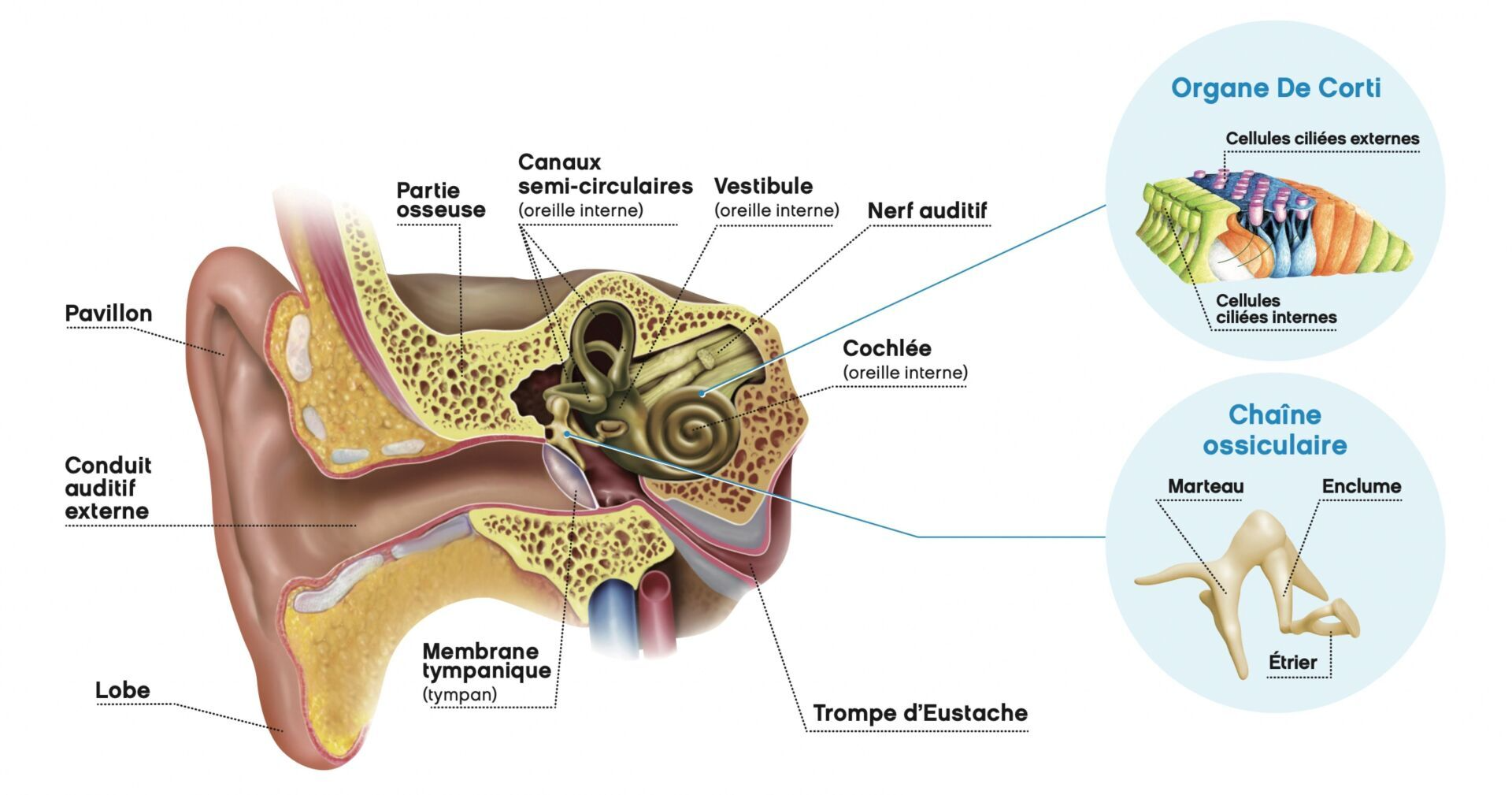
Hearing problems
Did you know that people wait on average 7 years before consulting for their hearing problems?¹
Presbyacousie
Presbycusis is progressive age-related hearing loss. It is characterized by losing the ability to hear and understand higher pitched sounds. Presbycusis often causes difficulty understanding speech in noisy environments. Usually, this hearing loss affects both ears symmetrically.
Occupational deafness
Occupational deafness is a permanent condition caused by prolonged exposure to noise at work. In Quebec, 400,000 workers are exposed to excessive noise as part of their work².
Noise workers who have a reduction in their hearing can take steps with the CNESST (even if the company is now closed or the person is retired).
Tinnitus
Tinnitus is a noise that only the affected person hears and which does not come from an external sound source. The type of sound heard and its intensity can vary from one person to another, as well as they can be continuous, temporary or pulsating.
Several solutions are available to reduce the effects of tinnitus.
One solution is sound therapy. This involves listening to different sounds or noises through headphones or hearing aids. This therapy involves introducing sound to teach the brain to leave the tinnitus as background noise. In this way the brain gives it less importance and the tinnitus can diminish or even disappear.
Sudden deafness
Sudden deafness is a rapid and sudden hearing loss appearing in less than three days. In the majority of cases, it occurs in only one ear. The affected person may hear tinnitus as well as feel like their ear is blocked. This hearing disorder should not be taken lightly; it is important to consult an ENT or audiologist ideally within 3 days of onset. Prompt treatment greatly increases the chances of recovery. A hearing test will be requested.
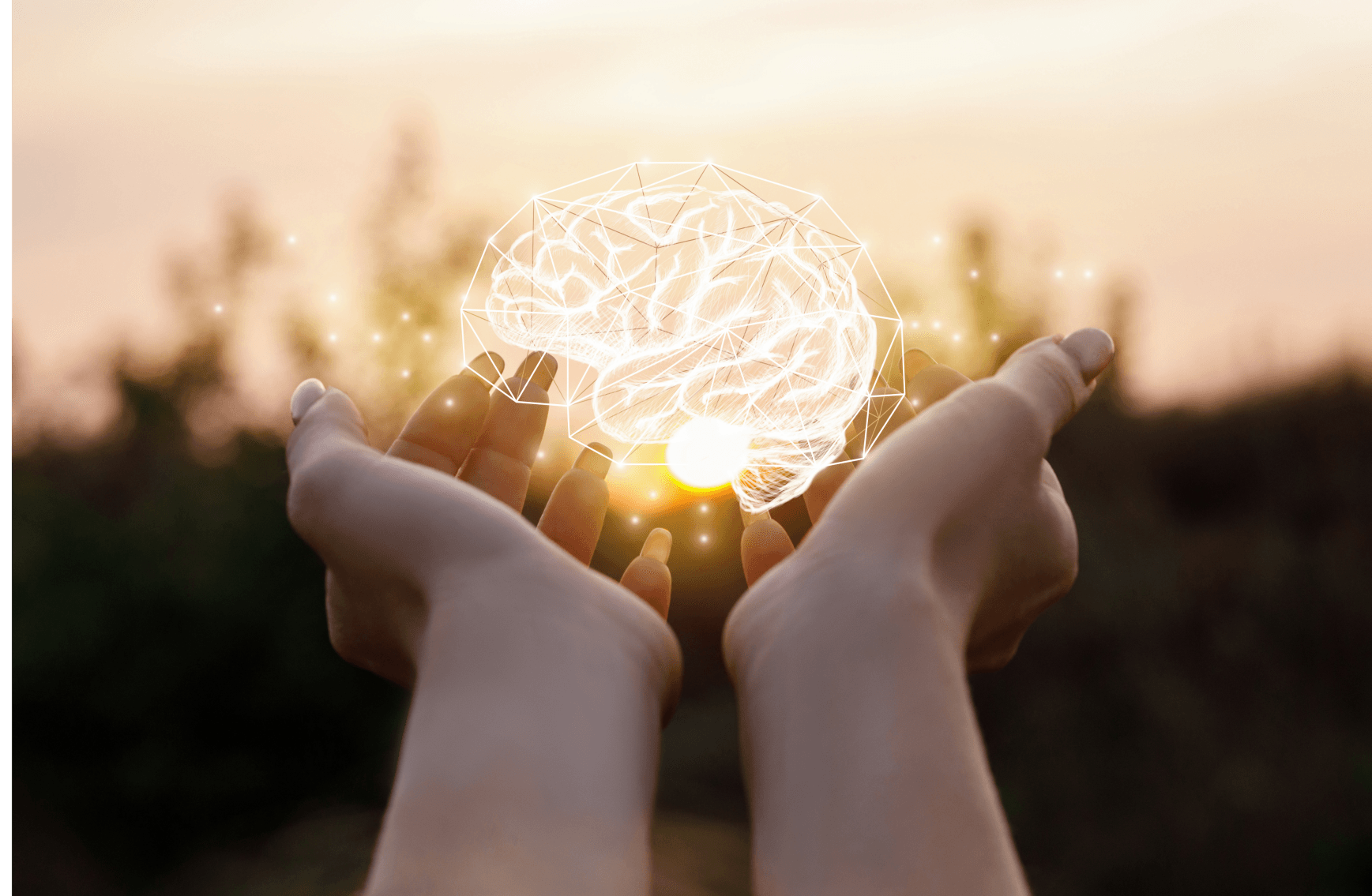

The impact of untreated hearing loss
Sensory deprivation
Sensory deprivation is the fact that when a person has untreated hearing loss, the information sent to the brain is diminished.
This deprivation then leads to a reduction in the brain's ability to understand speech. Indeed, the less information the brain receives from a part of the body, the less effective it will be in processing this information.
Who is at risk?
- Hearing impaired people who do not wear hearing aids.
- People who are deaf in both ears but only have one hearing aid. Sensory deprivation will be observed in the unaided ear.
Cognitive problems
Some studies show that people with untreated hearing loss are more likely to develop cognitive problems.
Decreased hearing skills can accelerate gray matter atrophy and increase the listening effort needed to understand speech. Hearing aids can improve hearing and they can also preserve the brain³.
Statistics
- From the age of 75, the risk of developing a degenerative disease of the Alzheimer type would be 2.48 times higher in subjects suffering from deafness with social embarrassment 4 If hearing problems were all treated in time, almost 1 case of dementia in 10 could be avoided5. Mild hearing loss doubles the risk of dementia 5.
Other impacts⁶
Hearing loss may be associated with diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
- Social isolation & restrictions on participationDecreased quality of lifeFatigueAnxietyDepressionDistressMobility problems, falls and other injuriesConcentration problemsReduced alertnessDecreased psychological and overall healthAnd many others
When to consult?
Untreated hearing loss increases the chances of suffering from anxiety, social isolation and increases the risk of depression. According to studies, deafness can also increase the risk of developing cognitive problems. On average, presbycusis (hearing loss associated with age) delays the onset of dementia by 5 to 10 years.
Indeed, with age we can have deafness which occurs gradually. This is presbycusis. Presbycusis is often characterized by difficulty hearing high-pitched sounds. People therefore have more difficulty in groups or they repeat words that are similar (Ten and six, thirteen and sixteen...).
- Difficulty understanding speech in a noisy environment Repeat Increased television volume Tinnitus Difference in hearing felt in both ears History of exposure to noise at work For prevention from the age of 45 years Sudden deafness Sound trauma or accident
WE ARE HERE TO HELP YOU
At the Lamarre & Lafantaisie hearing aid clinic, we offer a complete hearing aid service; Sale, installation, adjustment and repair of hearing aids. Printing socket for custom caps (For sleeping, swimming, musician, worker in noise). Free hearing screening test*
Certain models of hearing aids are covered by RAMQ, CNESST, Veterans Affairs or private insurance, depending on eligibility criteria.
Complete hearing assessment carried out by an independent audiologist who is a member of the OOAQ.